What is Prototypal Inheritance?
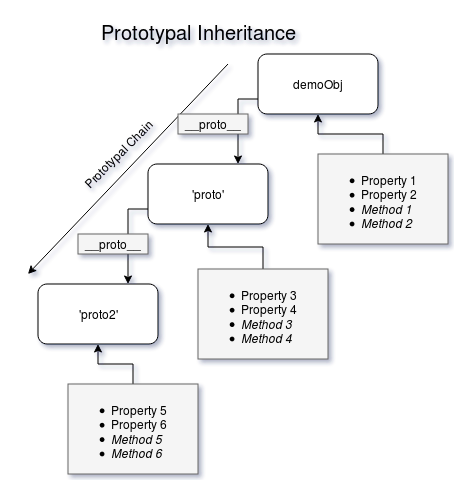
When a property or a method of an object is referenced in JavaScript, the JS engine looks for it within the object and along the prototype chain. Now what is the prototype chain. Every object in JavaScript has a _proto_ property which points to another object, say ‘proto’.
When a method or a property of an object is referenced, the JS engine looks for that method or property within the object. If not found, it then looks for that method or property within the ‘proto’ object referenced using _proto_ property
Now since ‘proto’ is also an object it also has a _proto_ property which points to another object, say ‘proto2’. The JS engine looks for the method or the property within ‘proto2’ if not found earlier and then further into ‘proto2’’s _proto_ property and so on.
How to access the prototype property (which points to the ‘proto’ object that is traversed in the prototypal chain) of an object?
var vehicle = {
color: 'black',
tyres: 4,
getColor: function() {
return this.color;
}
}
var car = {
color: 'red'
}
car.__proto__ = vehicle;
console.log(car.getColor());
console.log(car.tyres);
Output
red
4
In the above code we have set the proto property for the ‘car’ object to reference to the ‘vehicle’ object. Therefore when we call car.getColor, JS engine first looks for the getColor function in the ‘car’ object. When it does not find getColor there it looks in the object referenced via proto property ie the ‘vehicle’ object. The getColor is then executed. The this refers to the ‘car’ object and hence we get the output color as red and not black.
Likewise when we call car.tyres, since tyres property does on exist on the ‘car’ object, JS engine travels the prototype chain and returns the value. In this case it returns the value of the ‘tyre’ property as found in the ‘vehicle’ object.
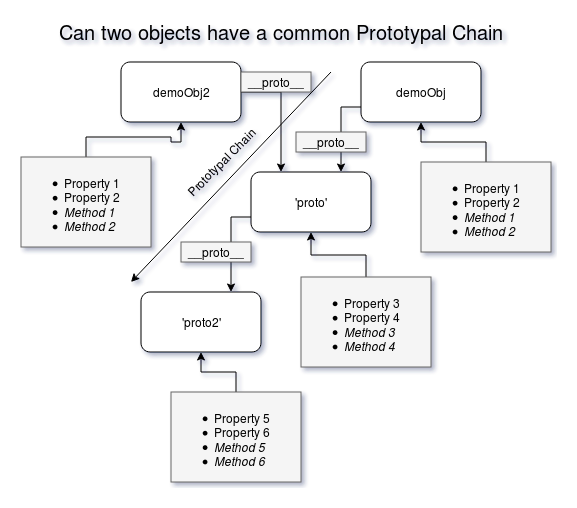
Can two objects refer the same object using their _proto_ property and thus have a common prototype chain?
Code
var car = {
color: 'red'
}
car.__proto__ = vehicle;
console.log(car.getColor());
console.log(car.tyres);
var cycle = {
tyres: 3
}
cycle.__proto__ = vehicle
console.log(cycle.getColor());
console.log(cycle.tyres);
Output
red
4
black
3
Where does the prototype chain end? At the base of every prototype chain in JavaScript is the base Object {} which provides various methods and properties for manipulating objects