Synchronous vs Asynchronous processing
While working on the data pipeline at SegmentOne, an early stage startup I worked with, we were able to improve the message consumption rate of RabbitMQ consumers by a factor of 10 by switching from a synchronous to an asynchronous execution model.
In this post, I am writing out my understanding of the difference resulting from the two models of execution - Synchronous and Asynchronous and what led to the performance improvement in our RabbitMQ consumers.
To highlight the difference between synchronous and asynchronous processing it is important to highlight the two categories of tasks that a section of code might perform
-
Compute Intensive - Heavy calculations such as calculating the hash, or encrypting a large file are tasks that could be classified as compute intensive. During a compute intensive task the processor is engaged and running the necessary calculations for the task at hand.
-
I/O Intensive - Reading and writing to a file, communicating over the network using sockets come under I/O intensive tasks. I/O tasks could take anywhere between a few milliseconds to a few seconds to complete depending upon various factors. During these tasks, the processor remains idle, such as during reading or writing to a file.
The key difference between synchronous and asynchronous processing is in what the processor does while it waits for an I/O task to complete.
In synchronous execution, the processor remains idle and waits for the I/O task to complete before executing the next set of instructions.
In the following code snippet we read from a file ‘test.txt’ synchronously. The file has the text ‘Hello World!’
var fs = require('fs');
const ioTimeStart = process.hrtime();
const contents = fs.readFileSync('test.txt', 'utf8');
const ioTimeEnd = process.hrtime(ioTimeStart);
console.log(contents);
console.log(`Time to complete the synchronous I/O task ${ioTimeEnd[1]/1000000} ms`);
console.log("After calling readFile synchronously");
Output
Hello World !
Time to complete the synchronous I/O task 0.178821 ms
After calling readFile synchronously
From the output we see that, the processor waits until the I/O task - which is reading from a file in this case - completes before moving to the next set of instructions. The order of output is the same as the order of the instructions in the code.
However if we were to read asynchronously from a file
var fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('test.txt', 'utf8', function(err, contents) {
if(err) {
console.log(err);
}
console.log(contents);
});
console.log('After calling readFile asynchronously');
After calling readFile asynchronously
Hello World !
The order of output changes when executing asynchronously. This is because the processor no longer waits for the I/O task to complete. After initiating the I/O task, the processor moves to the next instruction thus printing After calling readFile asynchronously to the console. Once the I/O task completes, it logs the contents of the file ‘test.txt` to the console. Nodejs manages asynchronous tasks using an event loop.
While the mental model to understand execution in an asynchronous environment is comparatively difficult to a synchronous environment where the instructions are executed in order, the asynchronous environment provides performance improvement by utilizing the processor when it would otherwise have remained idle.
Improving RabbitMQ performance
Synchronous execution
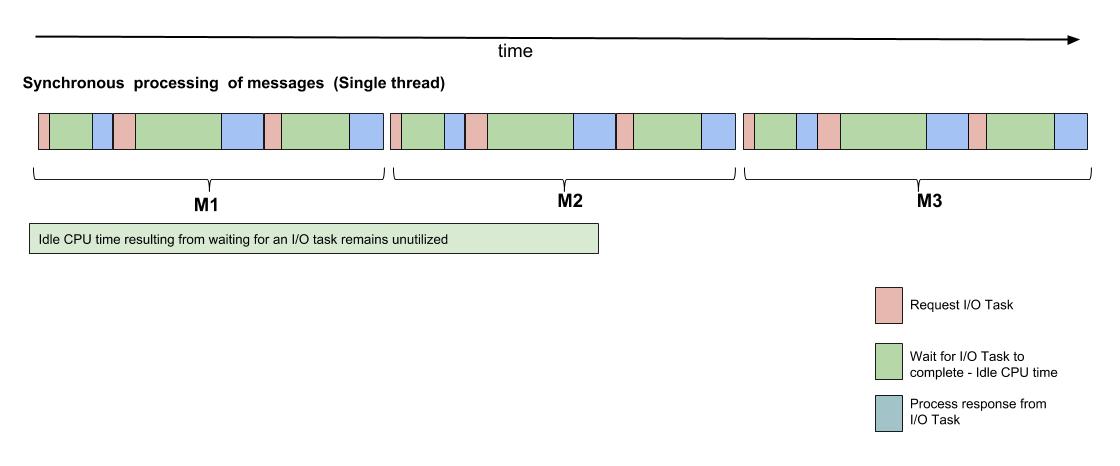
Each message processed by the RabbitMQ consumer involved a few I/O tasks (mostly database queries). In a synchronous model,
- The processor remained idle while the I/O tasks completed, as illustrated by the green block in the above diagram
- Messages could only be processed serially, the processing of a message could only begin after the processing of the preceeding message had completed
Asynchronous execution
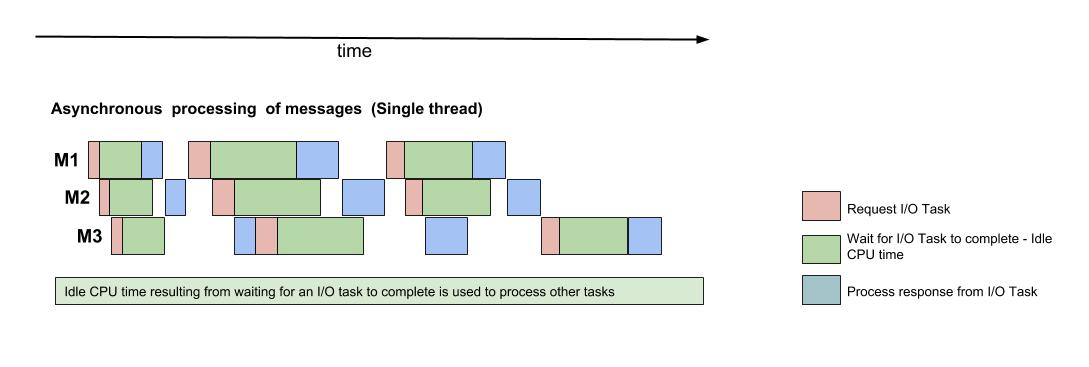
By switching to an asynchronous model
- The idle time when the processor was waiting for an I/O task to complete could be used to process other messages. In the diagram above, once the I/O request for M1 has been sent, the processor moves to processing the next messages in the queue.
- Parallel processing of messages - The processing of multiple messages could now be interleaved because of asynchronous execution